Case Study

Case presentation
A 2-year-old female patient presented with chief complaints of heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding for the last 7–8 months.
Medical history
- Last menstrual period persisted for seven days and needed a change of six pads per day.
- No intermenstrual spotting.
- No history of vaginal white discharge, backache, weight loss/gain, dyspareunia, or any urinary complaints.
- No known medical comorbidities.


Physical examination
| Body mass index (BMI) | 20.8 kg/m2 |
| Blood pressure | 122/81 mmHg |
| Pulse rate | 98 beats/minute |
Investigations
Blood work-up
| Pregnancy test | Negative |
| Haemoglobin (Hb) concentration | 9.4 g/dL |
| Mean packed cell volume (PCV) | 29.5gm% |
| Thyroid function tests | All components in normal range |
| Liver function tests | All components in normal range |
| Renal function tests | All components in normal range |

Imaging analysis
| Transvaginal sonography | Normal |
Assessment of menstrual blood loss

| Pictorial blood assessment chart (PBAC) scores | 203 |

Diagnosis: The patient was diagnosed with abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB).

Treatment: 500 mg Traneximic acid along with 250 mg Mefenamic acid, three times daily from day 1 to 5 of the menstrual cycle, for 3 months was prescribed.

Follow-up after 3 months: The mean Hb concentration improved to 11.7 g/dl, mean PCV improved by 15%, and the PBAC score dropped to 120..

Follow-up after 6 months: The mean Hb concentration further improved to 12.9 g/dl, mean PCV increased by 22%, and the PBAC score dropped further to 99.
Conclusion:
The concurrent use of Tranexamic acid and Mefenamic acid has proven to be effective in lowering PBAC scores and diminishing menstrual blood loss in cases of AUB. Treatment with Tranexamic acid and Mefenamic acid combination drug has demonstrated sustained efficacy over the long term.
References:
- Najam R, Agarwal D, Tyagi R, et al. Comparison of traneximic acid with a combination of traneximic acid and mefenamic acid in reducing menstrual blood loss in ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB). Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2010;4(5):3020-5..
- Lavadi RS, Venkatachalaiah R, Prasad M. Double Trouble: A Case Report of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding due to Both Central and Peripheral Pathology. International Journal of Applied and Basic Medical Research. 2022;12(2):134.
Case study

Efficacy of Mefenamic acid and Tranexamic acid in Management of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: A Case Report
A 40-year-old female patient with complaint of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Articles

Efficacy of Combination Therapy of Mefenamic acid and Tranexamic Acid in Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is excessive, prolonged heavy or frequent bleeding of uterine origin which is not due to pregnancy or any systemic or recognizable pelvic disease.
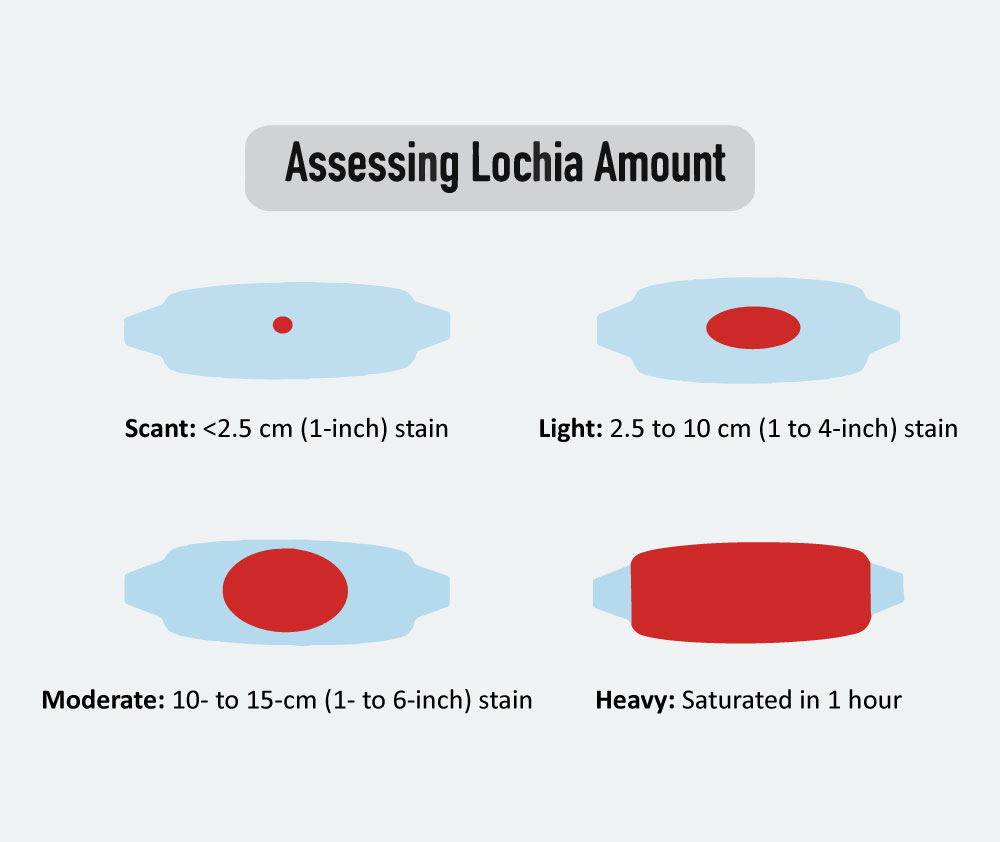
Assessment and Management of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB), a prevalent and distressing condition, is primarily defined by the patient's perception and observable signs like frequent pad or tampon changes, large clots, and disruption of daily activities.
Blog

Recent Updates on Prevalence and Burden of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding in Society
Heavy menstrual bleeding is a common disorder characterized by excessive blood loss that affects the quality of life of a female in physical, emotional, social and financial aspects.

The ICMR recommendations on the management of heavy menstrual bleeding
It is crucial to obtain a medical history for complete understanding of the current bleeding episode.