Blog

It is crucial to obtain a medical history for complete understanding of the current bleeding episode.
History taking should include:
- Age
- Number of pregnancies.
- Thorough menstrual history, including irregularities.
- Other medical conditions: thyroid disorder, jaundice, coagulopathy, etc.
- Intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD) use
- Medication use
- Lactation
The clinical examination should be aimed at assessing the underlying cause of uterine bleeding, and to exclude trauma or other aetiologies of bleeding.
Examination:
- General
- Assess pallor
- Evaluate body mass index (BMI)
- Systemic
- Cardiovascular system
- Respiratory system
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Local examination (where necessary and possible): per speculum (P/S) examination and per vaginum (P/V) examination
Women with heavy menstrual bleeding might require supportive treatment, and the treatment might comprise:
- Providing comfort and assurance
- Administration of Hematinics
- Use of Tranexamic acid during period of heavy bleeding

Blood work-up:
- Haemoglobin
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) with peripheral smear
- Bleeding time/Clotting time (BT/CT)
Management of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding at Primary Level
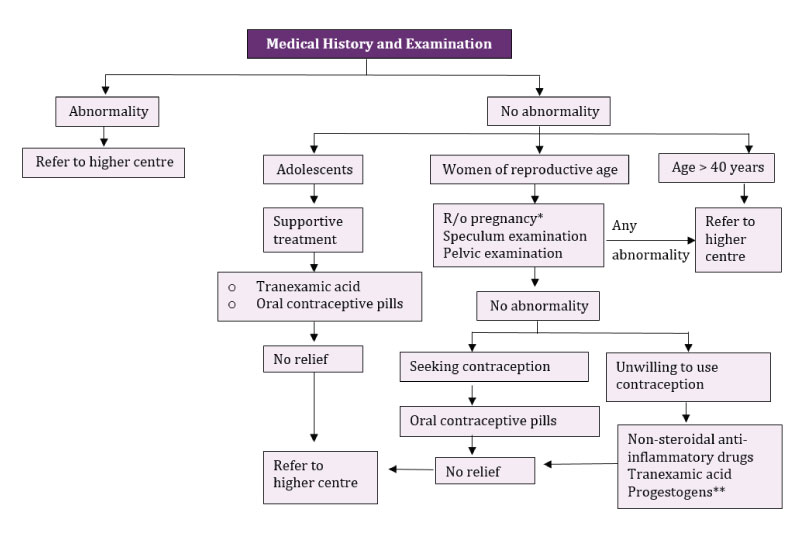
* R/o Pregnancy: In case of doubt, particularly in women of reproductive age group after receiving consent
** Amongst progestogens, Norethisterone offers the most effective haemostasis
Conclusion:
Obtaining history about menstrual health in primary care settings can enhance both outcomes and patient contentment. This ICMR recommended guideline offers a structure for the initial assessment and available treatment choices for women experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding.
Reference:
Indian Council of Medical Research. Standard Treatment Workflow (STW) for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB). Available online: https://main.icmr.nic.in/sites/default/files/Books/STW_Manual_v1.pdf. Accessed on:3rd Jan, 2024.
Blog

Recent Updates on Prevalence and Burden of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding in Society
Heavy menstrual bleeding is a common disorder characterized by excessive blood loss that affects the quality of life of a female in physical, emotional, social and financial aspects.
Articles

Efficacy of Combination Therapy of Mefenamic acid and Tranexamic Acid in Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is excessive, prolonged heavy or frequent bleeding of uterine origin which is not due to pregnancy or any systemic or recognizable pelvic disease.
Assessment and Management of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB), a prevalent and distressing condition, is primarily defined by the patient's perception and observable signs like frequent pad or tampon changes, large clots, and disruption of daily activities.
Case study

Combination therapy with Mefenamic acid and Tranexamic acid in heavy menstrual bleeding: An Interesting Case Report.
A 32-year-old female patient presented with chief complaints of heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding for the last 7–8 months.

Efficacy of Mefenamic acid and Tranexamic acid in Management of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: A Case Report
A 40-year-old female patient with complaint of heavy menstrual bleeding.