Article
Background:
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is excessive, prolonged heavy or frequent bleeding of uterine origin which is not due to pregnancy or any systemic or recognizable pelvic disease.
Around 28% of females consider their menstrual bleeding as excessive and plan their social activities according to their menstrual cycle.
Approximately 10% of the working women take time off due to excessive menstrual blood loss.
Menstrual fluid in menorrhagia has increased fibrinolytic activity.
Synthetic antifibrinolytics reduce menstrual blood loss. Tranexamic acid is 6-10 times more potent than other synthetic antifibrinolytic agents and lead to 45-60% reduction of menstrual bleeding.
A study on Tranexamic acid and Mefenamic acid therapy:
Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics conducted a prospective trial.
It included 670 patients with abnormal uterine bleeding of which 110 had heavy menstrual bleeding.
Patients were in the age group of 12-45 years.
Married females having endometrial thickness of less than 5mm in transvaginal sonography were also included.
The Patients were divided in T and TM groups.
T-group (500 mg Tranexamic acid T.I.D from day 1-5 of menstrual cycle)
TM-group (500 mg Tranexamic acid and 250 mg Mefenamic acid ) T.I.D from day 1-5 of menstrual cycle
Study Findings:
Tranexamic acid reduced menstrual bleeding and is a highly effective heamostatic agent.
Tranexamic acid and Mefenamic acid showed great potential in the reduction of dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Tranexamic acid was found to be efficacious in treatment of menorrhagia and its combination with Mefenamic acid has shown promising results.
Conclusion:
Tranexamic acid alone or in combination with mefenamic acid is effective in reduction of menstrual bleeding.
The combination of Tranexamic acid and mefenamic acid is efficacious it is recommended for providing symptomatic improvement in the general health of the patients and for reduction of blood loss associated with ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Reference:
Najam R, Agarwal D, Tyagi R, Singh S. Comparison of traneximic acid with a combination of traneximic acid and mefenamic acid in reducing menstrual blood loss in ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB). Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2010;4(5):3020-5.
Articles
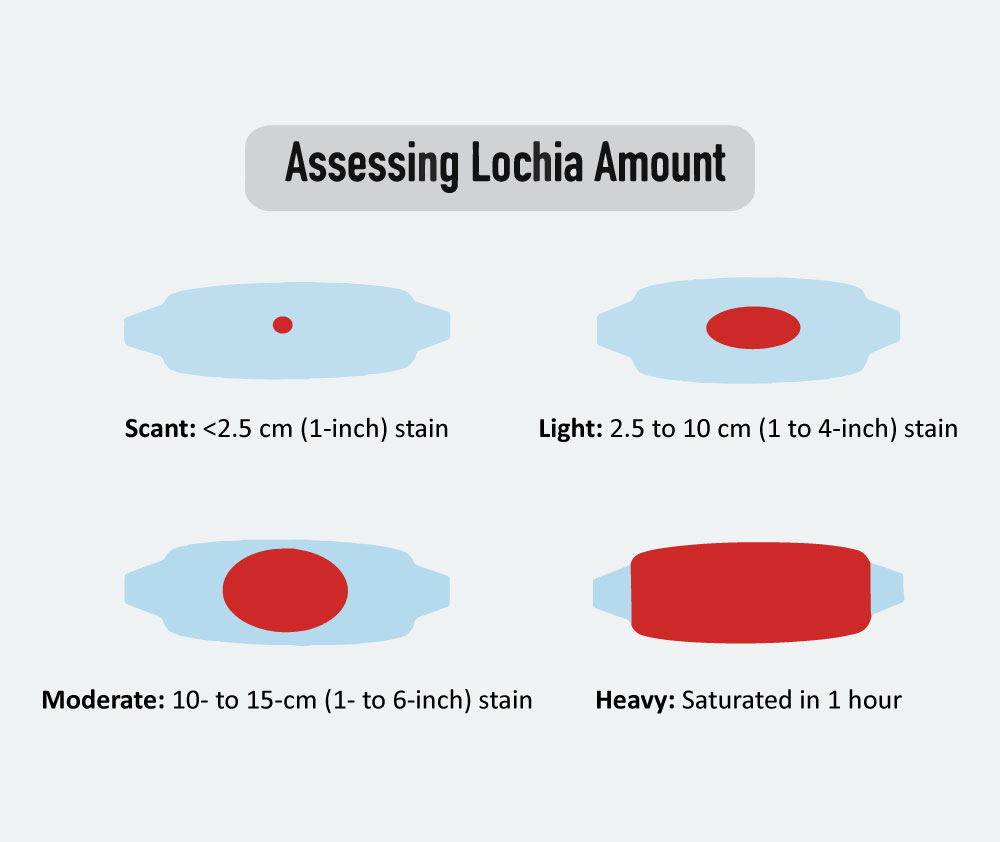
Assessment and Management of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB), a prevalent and distressing condition, is primarily defined by the patient's perception and observable signs like frequent pad or tampon changes, large clots, and disruption of daily activities.
Case study

Combination therapy with Mefenamic acid and Tranexamic acid in heavy menstrual bleeding: An Interesting Case Report.
A 32-year-old female patient presented with chief complaints of heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding for the last 7–8 months.

Efficacy of Mefenamic acid and Tranexamic acid in Management of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: A Case Report
A 40-year-old female patient with complaint of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Blog

Recent Updates on Prevalence and Burden of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding in Society
Heavy menstrual bleeding is a common disorder characterized by excessive blood loss that affects the quality of life of a female in physical, emotional, social and financial aspects.

The ICMR recommendations on the management of heavy menstrual bleeding
It is crucial to obtain a medical history for complete understanding of the current bleeding episode.